Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) simulates human intelligence in machines, enabling tasks like learning, reasoning, and decision-making. As of August 2025, AI adoption has hit 78% of organizations worldwide, up from 72-78% in 2024, driven by tools that boost productivity and innovation.
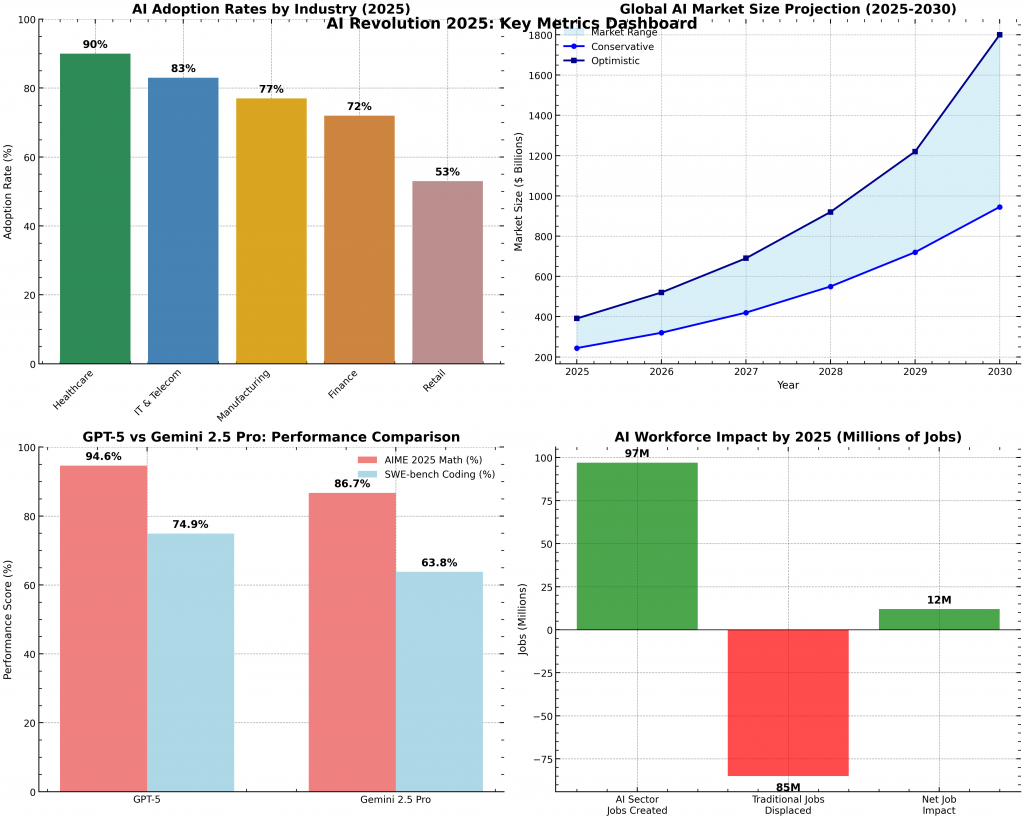
The global AI market now stands at $391 billion in 2025, projected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2030 at a 29-38% CAGR. Whether you’re a beginner curious about AI’s role in daily life or seeking practical examples, this post breaks it down simply. Let’s explore how AI is reshaping our world—starting with its core principles.

Key Finding: AI isn’t just tech hype—it’s a $391B powerhouse creating 97 million jobs while raising ethical questions.
Core Principles of AI
AI rests on foundational concepts that mimic human thinking. These principles form the backbone of modern applications.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) lets systems learn from data to improve without direct programming. It includes supervised (labeled data for predictions), unsupervised (pattern-finding in unlabeled data), and reinforcement learning (trial-and-error via rewards).
Updates for 2025 highlight foundation models like LLMs, trained on vast datasets for tasks like text generation. Prompt engineering—crafting precise inputs—has become key for accuracy.
For example, Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in text generation and understanding.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows machines to process human language, powering chatbots and translators. Advancements like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) reduce hallucinations by integrating real-time data. In 2025, NLP integrates with multimodal AI for handling text, images, and audio together.
Robotics and Other Key Areas
Robotics merges AI with hardware for physical tasks, like autonomous drones. Other essentials include deep learning (neural networks) and transfer learning (adapting models efficiently).
New emphases: MLOps for streamlined deployment and explainability to make AI decisions transparent.
Recent Advancements in AI (2023-2025)
AI has leaped forward since 2023, with models becoming more capable and integrated.
Generative AI Revolution
Generative AI creates new content by learning patterns from data, with tools like ChatGPT, DALL-E for images, and Sora for videos becoming mainstream. Adoption jumped to 71% in organizations by 2024, focusing on business outcomes like efficiency.
Multimodal and Agentic AI
Multimodal AI processes multiple data types (text, images, audio), as seen in Google’s Gemini. Agentic AI enables autonomous actions, like workflow automation, though it still needs human oversight.
Breakthrough Models: GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5
OpenAI’s GPT-5, launched August 2025, excels in reasoning with a 400,000-token context and 74.9% coding accuracy on SWE-bench . Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro offers a 1-million-token window and native multimodal support, scoring 63.8% on coding benchmarks
Domain-Specific AI Applications
Specialized models tailor AI to industries, improving diagnostics in healthcare or risk assessment in finance. Advancements in reasoning, like OpenAI’s o1, support complex tasks in science and law.

AI Adoption and Market Statistics
AI adoption has accelerated, with 83% of companies prioritizing it in strategies. Here’s a summary of key data:
| Metric | 2025 Value | Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Global Adoption | 78% | 80% by year-end |
| Market Size | $391B | $1.8T by 2030 |
| CAGR | 29-38% | – |
| AI Users | 378M | – |
| Generative AI | $62.72B | 41.53% CAGR |
These figures underscore AI’s economic impact, with revenue growth up to 15.2% from generative applications.
AI in Key Industries
AI’s applications have expanded with specific adoption rates:
In education, AI enables personalized tutoring ; in media, it boosts content creation.
AI Safety and Alignment
AI safety focuses on preventing risks like misuse or biases, now encompassing sociotechnical factors. Alignment ensures AI matches human values, but issues like “alignment faking” in LLMs persist.
Developments include formal guarantees from workshops like Vienna 2024 . For beginners: Think of safety as AI’s “seatbelt”—essential for trust.
Key Finding: Safety gaps, like prompt injection, demand interdisciplinary fixes for reliable AI.
Workforce Impact of AI
AI displaces 85 million jobs by 2025 but creates 97 million new ones, netting positive growth. 75% of workers use AI, with 59% needing reskilling.
Vulnerable roles: Data entry, admin (45% hiring drop) . Growing areas: Cybersecurity, AI development. Companies like IBM are training millions
Ethical Considerations and Regulations
AI raises concerns like bias, where unfair data leads to discriminatory outcomes. Responsible AI emphasizes ethics, transparency, and accountability.
The EU AI Act, effective August 2024, mandates risk management for high-risk uses. Companies now focus on guardrails to prevent misuse.
Key Finding: Ethical AI is crucial—bias mitigation and regulations like the EU AI Act ensure safe deployment.
Future Trends for 2025 and Beyond
AI agents will automate workflows, with multimodal tech dominating. Focus on low-code tools and sustainability.
By 2030, 30% of jobs could automate, but human-AI collaboration will thrive.
FAQ
What is the difference between GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5?
GPT-5 excels in reasoning (94.6% on math benchmarks), while Gemini offers a larger context window for multimodal tasks.
How is AI affecting jobs in 2025?
It displaces routine roles but creates more in tech and healthcare, with 97 million AI jobs projected.
What are AI’s environmental concerns?
High energy and water use; new laws mandate mitigation
How can beginners start with AI?
Try tools like ChatGPT and learn basics via free courses.
Is AI safe to use?
With proper alignment and regulations, yes—but ongoing research addresses risks like bias.
Conclusion
This 2025 update to the AI Fundamentals blog integrates cutting-edge insights, from GPT-5 breakthroughs to workforce transformations, while preserving beginner-friendly explanations. With 78% adoption and a focus on ethics, AI is evolving responsibly—stay ahead by exploring tools like Gemini. Share your AI experiences in the comments, subscribe for updates, or check related reads on ethical AI. As of Tuesday, August 12, 2025, this guide equips you for the AI era.
References
Discover more from My Tricky Notes
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
